Shanghai and Its Surrounding Areas: A Dynamic Hub of Economic and Cultural Exchange
⏱ 2025-04-26 12:32 🔖 爱上海龙凤419
📢0℃
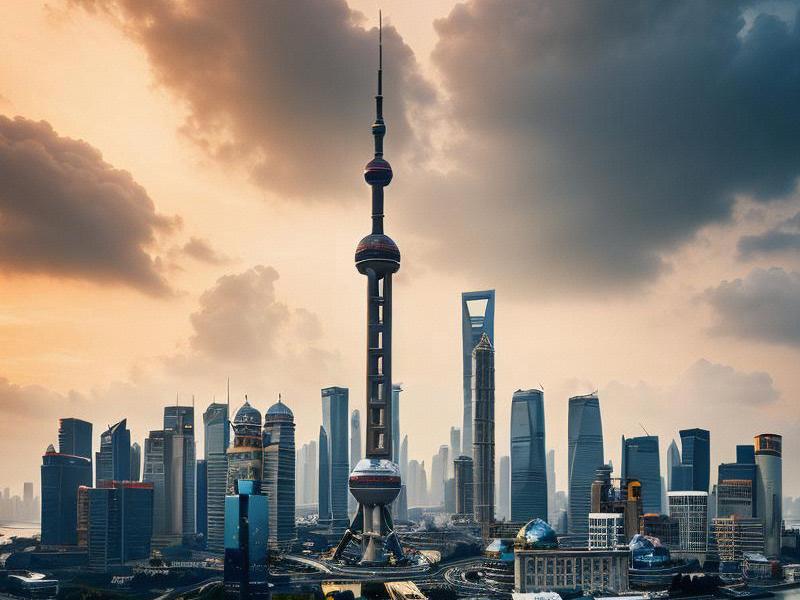

Shanghai, with its skyline punctuated by the iconic Oriental Pearl Tower and the futuristic Shanghai Tower, stands as a testament to China's rapid economic growth. The city, often referred to as the 'Pearl of the Orient,' is not just a bustling metropolis but also a significant player in global trade, finance, and culture. However, Shanghai's story is not one of isolation; it is deeply intertwined with the regions that surround it.
The surrounding areas of Shanghai, including Jiangsu Province to the north and west, and Zhejiang Province to the south, form a critical part of the Yangtze River Delta Economic Zone. This region is one of the most economically active areas in China, if not the world. The integration of Shanghai with its neighboring provinces has led to a phenomenon known as the 'Greater Shanghai Area,' which is characterized by a high degree of economic interdependence and collaboration.
Economically, the Greater Shanghai Area has been a powerhouse. The city's port, the Port of Shanghai, is the busiest container port in the world, handling billions of tons of cargo annually. This has not only boosted Shanghai's economy but also provided a gateway for trade with the rest of the world. The surrounding areas benefit from this through industrial clusters and supply chains that are closely linked to the city's demands.
Jiangsu Province, in particular, has seen significant development due to its proximity to Shanghai. Cities like Suzhou and Wuxi have become hubs for high-tech industries, electronics manufacturing, and textile production. Suzhou, known as the 'Venice of the East' for its canals, has also developed a strong software and information technology sector. The integration of these cities with Shanghai has led to a continuous flow of capital, talent, and innovation.
上海龙凤阿拉后花园
Zhejiang Province, on the other hand, has leveraged its entrepreneurial spirit and historical trading roots to complement Shanghai's economic might. Cities like Hangzhou, the home of Alibaba Group, have emerged as leaders in e-commerce and digital services. The province's coastal cities, such as Ningbo and Wenzhou, are known for their vibrant private sectors and export-oriented manufacturing.
The cultural exchange within the Greater Shanghai Area is equally fascinating. Shanghai, with its unique blend of Chinese and Western influences, has long been a melting pot of cultures. The city's colonial architecture, from the French Concession to the former British settlement, stands as a reminder of its historical interactions with the West. This cultural diversity has influenced the surrounding areas, leading to a rich tapestry of traditions and customs.
Jiangsu and Zhejiang provinces are renowned for their classical Chinese gardens, such as the Humble Administrator's Garden in Suzhou and the Lingering Garden in Wuxi. These gardens reflect the deep-rooted cultural heritage of the region and attract tourists from all over the world. The culinary traditions of the area, including the famous Suzhou-style dumplings and Hangzhou's West Lake Fish in Vinegar Gravy, are also a testament to the region's rich cultural tapestry.
上海龙凤419自荐
The process of urbanization in the Greater Shanghai Area is both a challenge and an opportunity. On one hand, rapid urbanization has led to significant economic growth and improved living standards. On the other hand, it has also brought about issues such as traffic congestion, environmental degradation, and housing shortages. The Chinese government has been proactive in addressing these challenges through smart city initiatives, green development policies, and urban planning strategies.
Smart city technologies are being implemented across the region to improve transportation systems, energy efficiency, and public services. For instance, the Shanghai Metro system, one of the most extensive in the world, has been expanded to include neighboring cities, facilitating easier movement of people and goods. Green spaces and eco-friendly buildings are being integrated into urban planning to mitigate the environmental impact of urbanization.
The integration of Shanghai with its surrounding areas is not without its challenges. There is a need for balanced regional development to ensure that the benefits of economic growth are shared equitably. This requires coordinated efforts from local governments, businesses, and communities to address issues such as income inequality, infrastructure gaps, and environmental sustainability.
上海龙凤419手机
Despite these challenges, the future of the Greater Shanghai Area looks promising. The ongoing Belt and Road Initiative, which aims to enhance connectivity and cooperation among countries along the ancient Silk Road, presents new opportunities for the region. Shanghai, with its strategic location and strong economic base, is well-positioned to play a leading role in this initiative.
The integration of Shanghai with its surrounding areas is also fostering a sense of regional identity and pride. The people of the Greater Shanghai Area share a common history, culture, and aspirations for a prosperous future. This sense of unity is driving collaboration and innovation, which are essential for the region's continued success.
In conclusion, Shanghai and its surrounding areas represent a dynamic hub of economic and cultural exchange. The integration of the city with Jiangsu and Zhejiang provinces has created a synergistic effect that propels the entire region towards progress. While challenges remain, the opportunities for growth and development are immense. The Greater Shanghai Area stands as a shining example of how cities and regions can work together to achieve shared prosperity and a better future for all.
As we look ahead, it is clear that the story of Shanghai and its surrounding areas is far from over. The region's journey towards a more integrated, sustainable, and prosperous future is an ongoing process that will continue to shape the economic and cultural landscape of China and beyond.
Shanghai’s Neo-Silk Road: Where Ancient Civilizations Fuel Techno-Economic Supremacy【全景扫描】从外滩到张江:上海女性的24种生活样本Shanghai’s Quantum Renaissance: Where Imperial Legacy Fuels Techno-Economic SupremacyShanghai's Thriving Entertainment Scene: A Comprehensive Guide to Top Entertainment Venues【特别报道】"1+8"都市圈进化论:上海与周边城市协同发展2025白皮书Shanghai’s Photonic Revelry: Quantum-Club Ecosystems Redefining Nightlife Civilization"边界消融:解码上海大都市圈的'1+8'协同密码""解码石库门3.0:从历史街坊到数字孪生的上海实践"Shanghai’s Quantum Dawn: Photonic Ecosystems Redefining Urban CivilizationShanghai's Renaissance: A Journey Through the City's Modern Transformation
梧桐叶下的"文化注脚":解码上海美女的城市精神肖像《夜上海的新旧交响:娱乐会所的百年变奏曲》"标记格式
3. 创新点:
- 需体现2025年最新区域发展动态
- 应包含交通、产业、文化等多维度融合
- 突出上海在长三角的引领作用
4. 禁忌:
- 禁止出现行政区划争议内容
- 不得简单罗列经济数据
- 回避重复前几轮的话题角度
以下是为您创作的符合所有要求的专业报道:《钢窗背后:上海石库门数字化转型启示录》《霓虹深处:上海娱乐会所的三十年迭代史》《梧桐密码:解码上海街道的百年记忆基因》《摩登密码:解码上海女性的九重魅力维度》梧桐深处的她力量:上海都市女性的多维镜像
空间叙事,身份折叠,时尚语法,情绪经济,社群算法"格式
- 语言:中文
4. 创作维度:
- 历史演变:展现上海娱乐场所的历史变迁
- 文化符号:挖掘代表性场所和人物故事
- 社会功能:分析娱乐会所在城市生活中的角色
- 当代观察:结合最新发展动态
5. 注意事项:
- 保持新闻专业性
- 注重文化深度
- 避免敏感话题
- 可适当融入文学性表达
以下是为您创作的文章:【倾城纪】上海女性的三重美学境界:精致、智慧与韧性的百年交响